Setup Probo.CI for a Drupal site that uses GitHub.
Probo.CI is here to make your development workflow more fluid. We want you to be able to configure Probo.CI to fit your project’s needs. Below is a step by step example of a standard Drupal site install with GitHub. This walkthrough does not use all the available parameters provided by the Drupal plugin, but you can see more available parameters in the Probo Drupal Plugin documentation.
You can find this Probo.CI example repository here.
You will need:
- A standard Drupal site with a MySQL database
- Your code stored in a repository on GitHub
Sign in and Sync up.
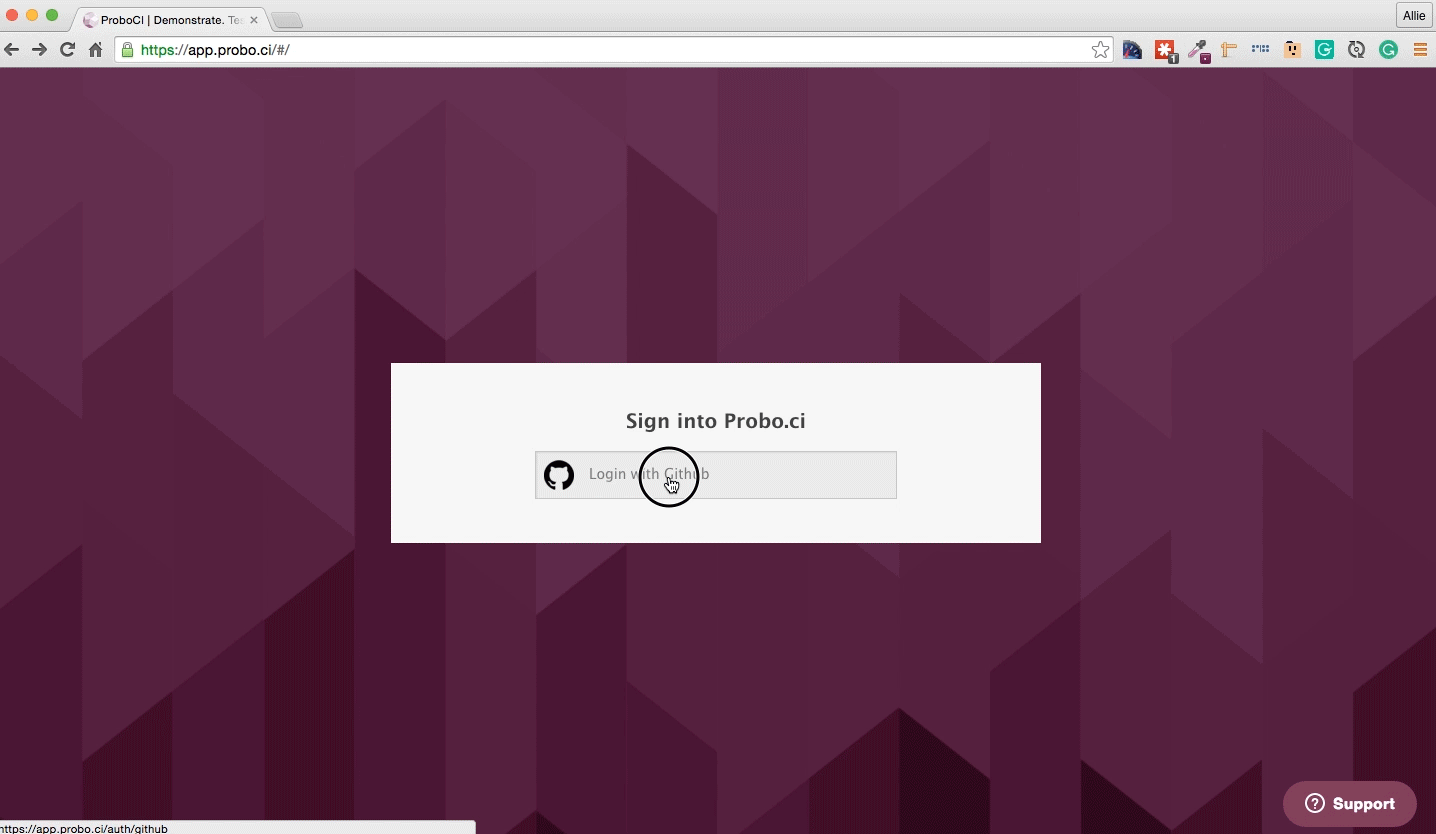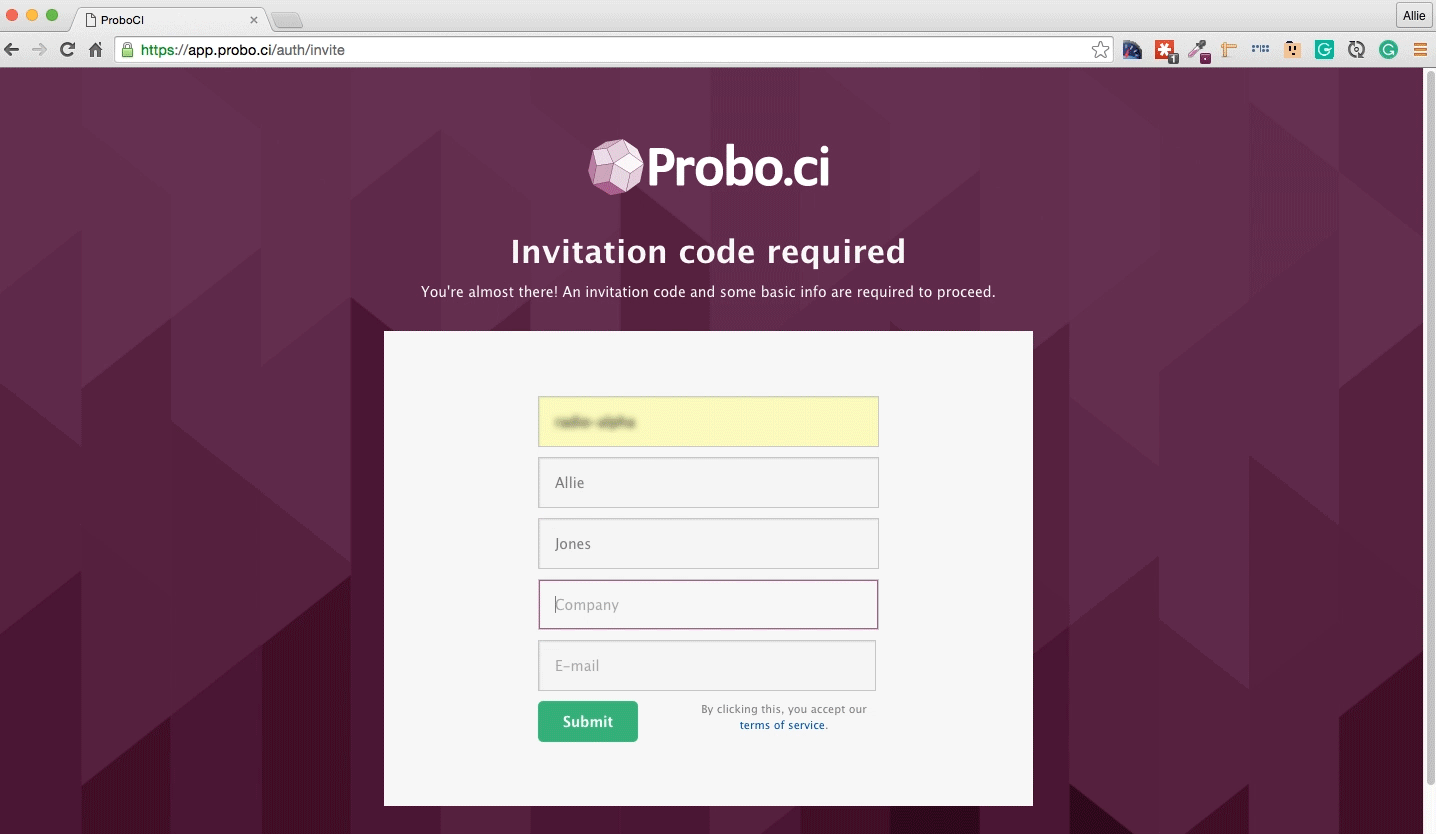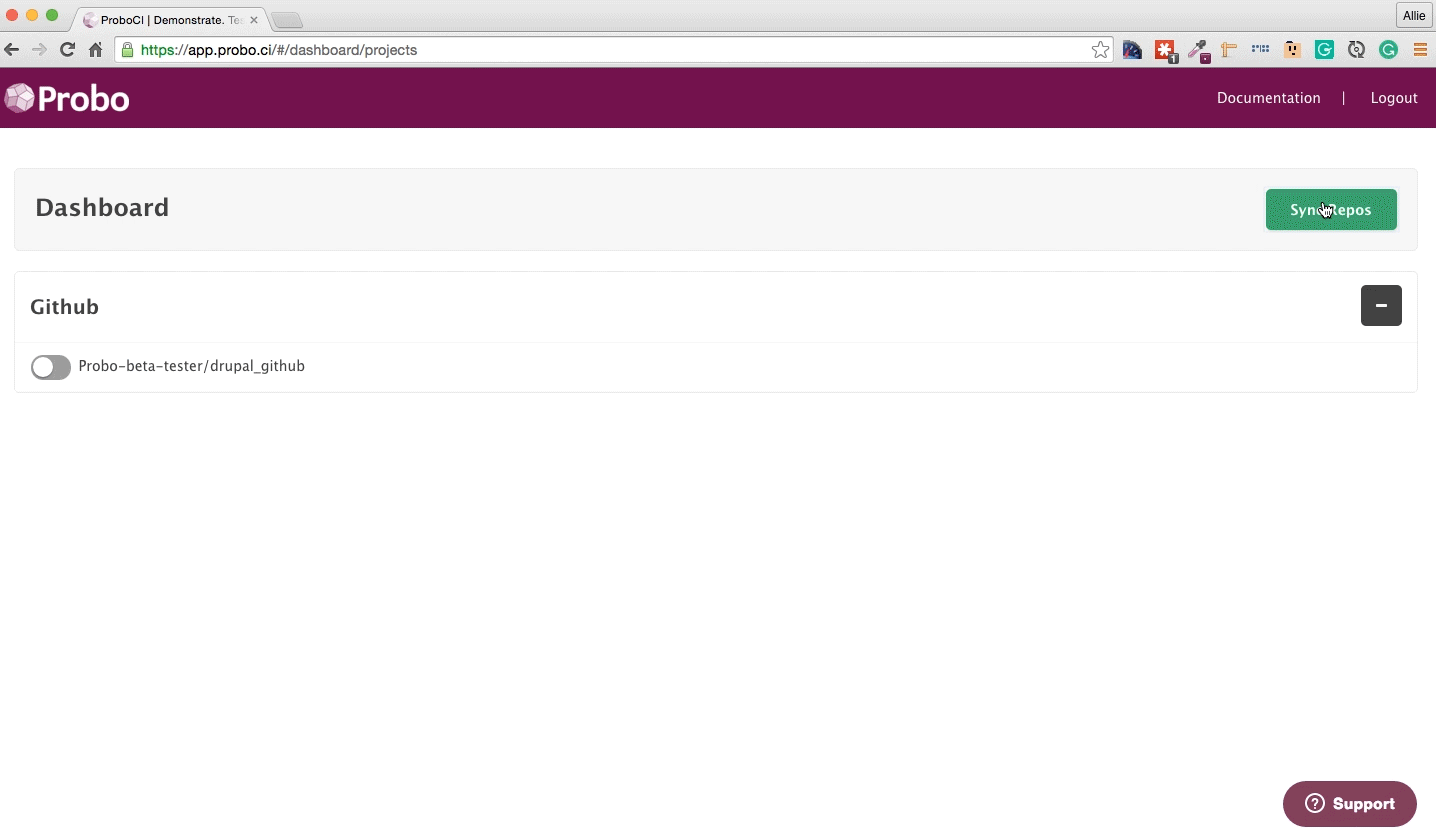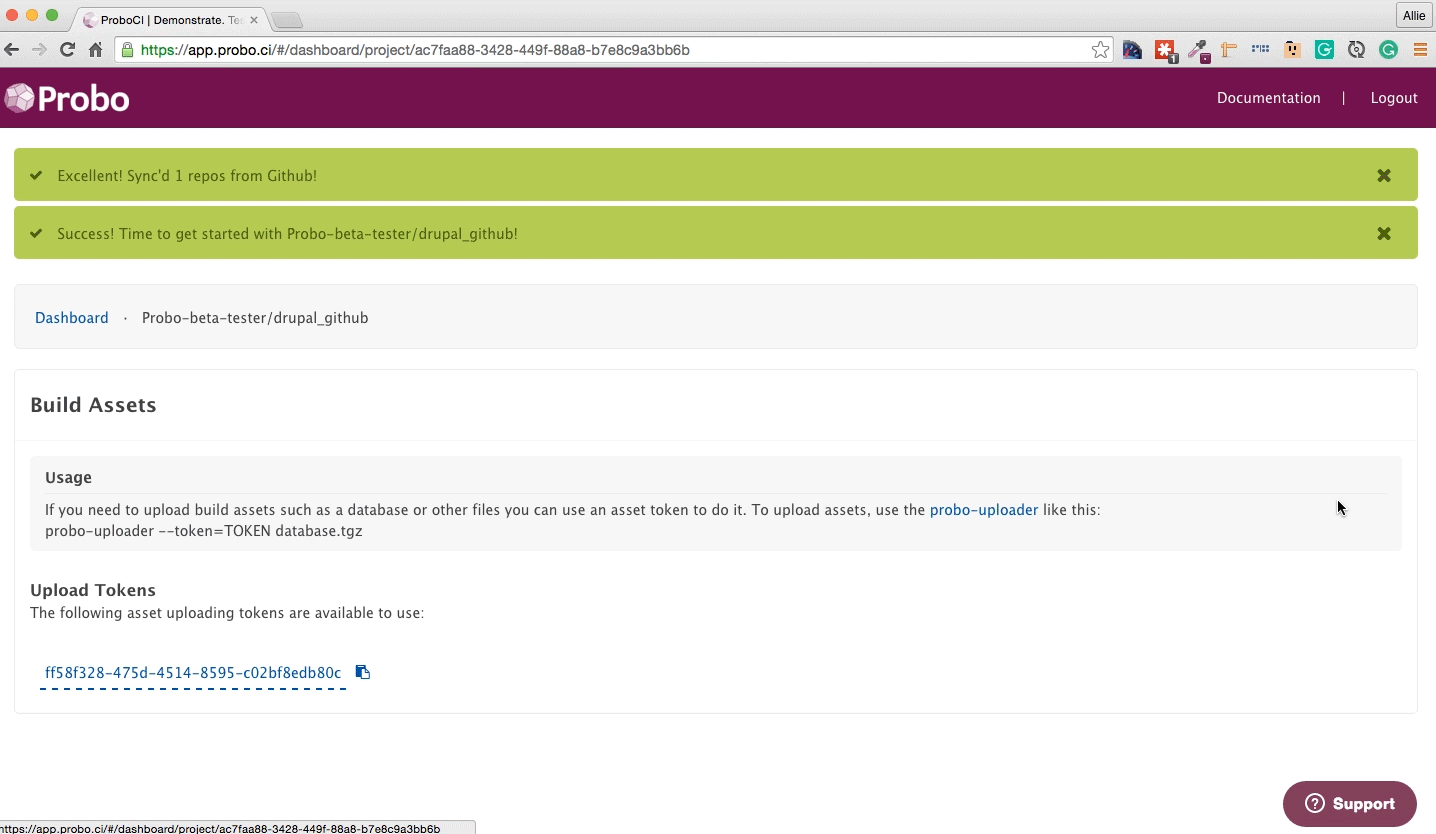
Step 1: Sign into the Probo app and authenticate GitHub.
Go to the Probo app and click on the Login to GitHub button. Once you get to GitHub, click ‘Authenticate application’.
Step 2: Sync your GitHub Repos.
Your GitHub repositiories will be synced automatically. You can always click the ‘Sync Repos’ button at the top right corner if you need to manually update your dashboard. Click on the button next to each repo that you want to use with Probo CI.
Prepare your Database.
You will need to import your project’s database with the Probo Uploader, a CLI tool. You will first import your database, then you will declare the database file in a .probo.yaml file. We will use the Drupal plugin to revert features, run database updates, and clear caches. (Cache all the things!)
Step 3: Sanitize your database (optional).
Although we compress and encrypt your database, it is always best practice to sanitize and compress your files.
Very Important: Do not do this on a production database.
Drush sql-sanitize will reset passwords and email addresses in the user table and truncate Drupal’s sessions tables. It is extremely important to note that you do not do this on a production database.
drush sql-sanitizeStep 4: Use Drush to get and compress your database in a sql file.
If you wish to compress your database you’ll need to use gzip. Other zip files won’t work.
drush sql-dump | gzip > dev.sql.gzStep 5: Install the Probo Uploader on your machine with npm.
You will need Node.js for the Probo.CI Uploader. Install node.js and npm if you don’t already have them.
sudo npm install -g probo-uploaderStep 6: Upload your database to the Probo.CI app.
Each repository will have it’s own token. You can find your project’s token on the dashboard of the Probo.CI app.
probo-uploader --token=[your-token] dev.sql.gz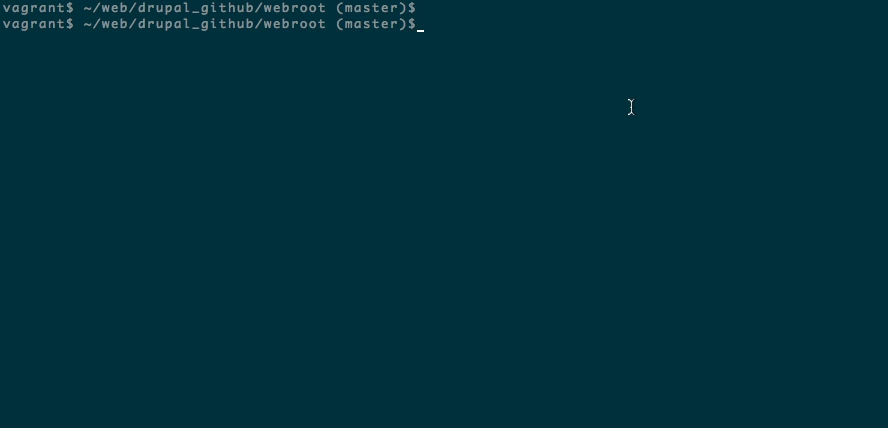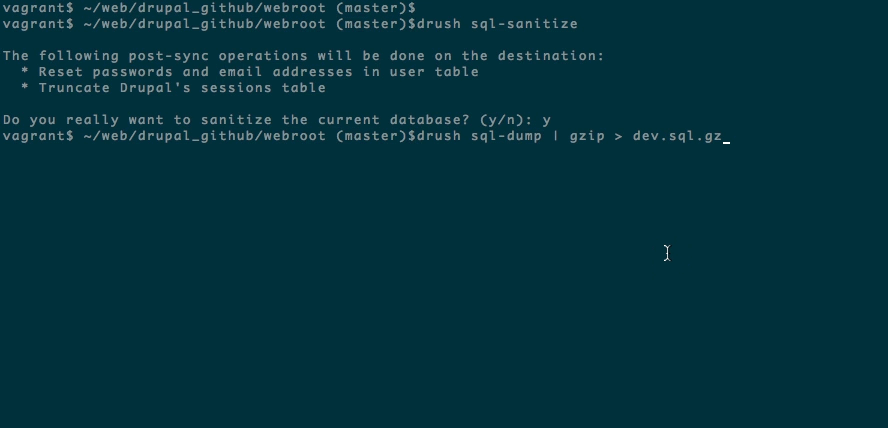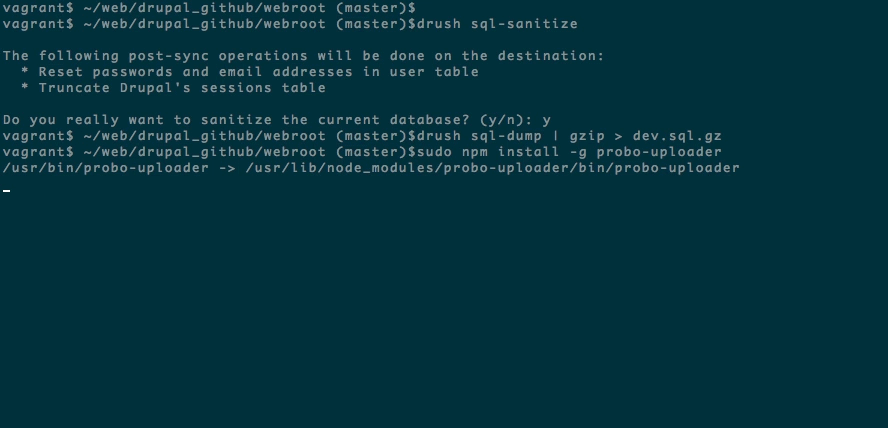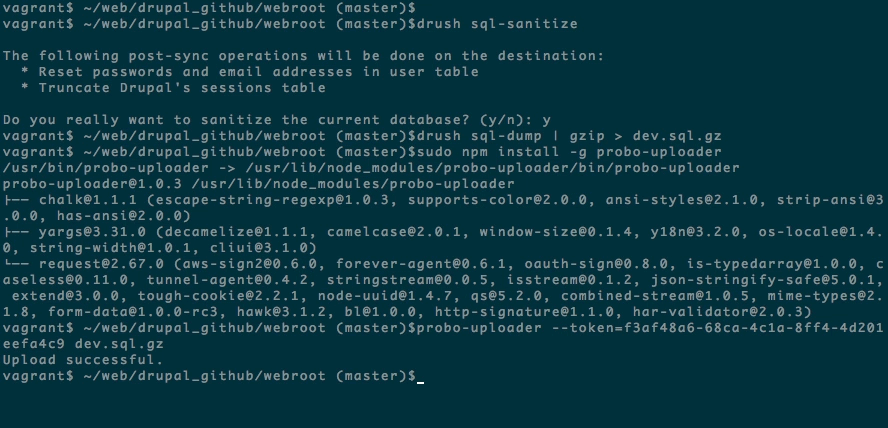
Define your website configuration for Probo.
The real magic of Probo.CI is automating pull requests to create test environments for you. In order to do that, you will need to add a few things to your project.
Step 7: Create a new branch.
cd into your project and create a new branch.
git checkout -b probo-buildStep 8: Create your .probo.yaml file.
You will need a .probo.yaml file in the root of your directory. You can task Probo.CI to run any number of build steps. Each step is a runnable plugin, and will get a status update sent to hosted repository for the commit. * Remember that indentation and spacing is important for yaml files.
vim .probo.yamlStep 9: Declare your assets and build your steps.
Tell Probo.CI what database you are going to use for your Probo.CI builds. Add in your parameters as steps. You can read more in the docs about different parameter options.
assets:
- dev.sql.gz
steps:
- name: Probo.CI site setup
plugin: Drupal
database: dev.sql.gz
databaseGzipped: true
databaseUpdates: true
revertFeatures: true
clearCaches: trueStep 10: In your new branch probo-build, add and commit your files to your remote origin.
git add .probo.yaml
git commit -m "Adding .probo.yaml."
git push -u origin probo-build 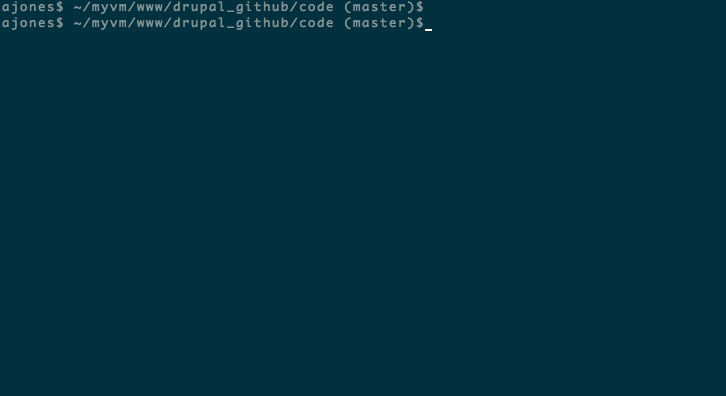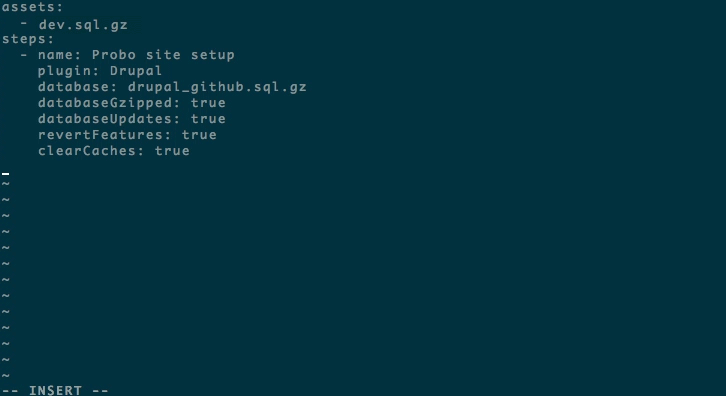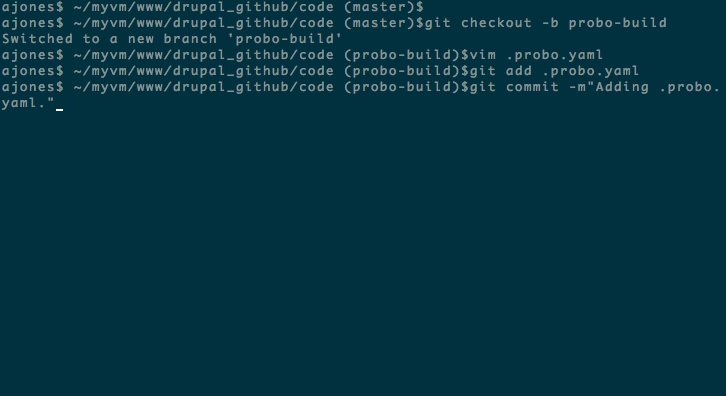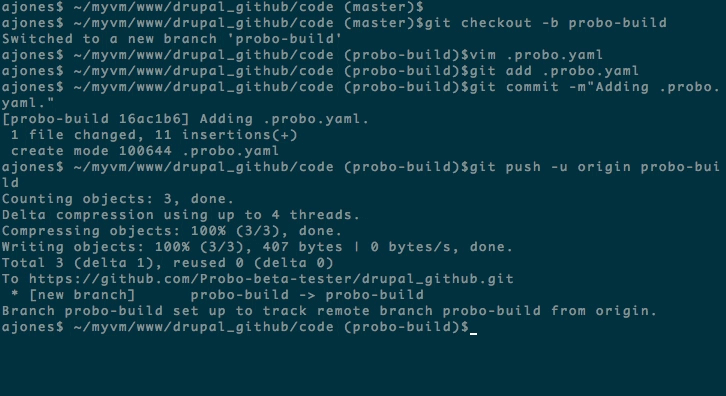
View your build.
Step 11: Go to your GitHub account. You will see your new branch inside your project. https://github.com/Probo-Demos/drupal_github
Step 12: Create a pull request.
Click ‘New Pull Request’.
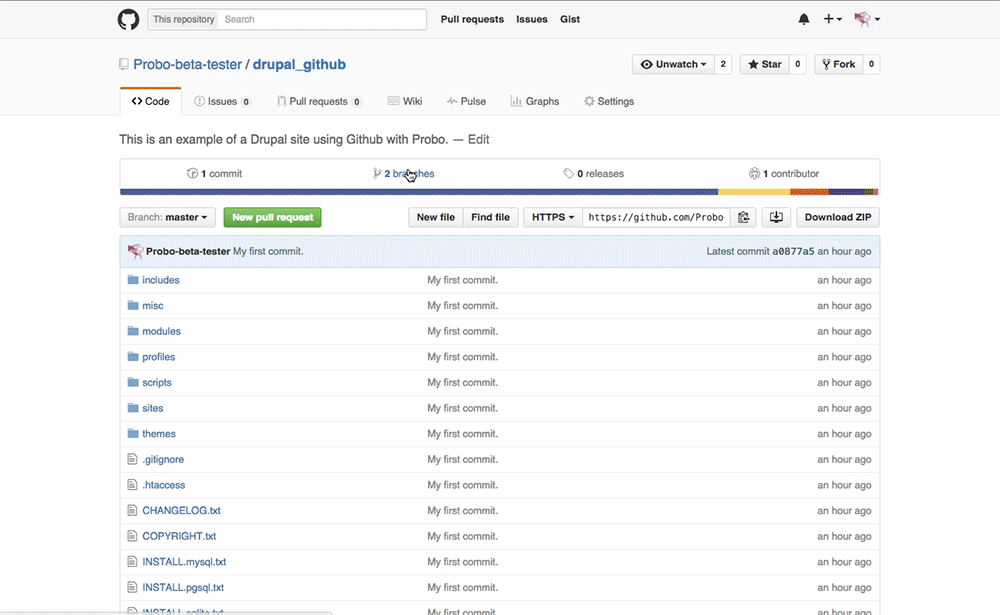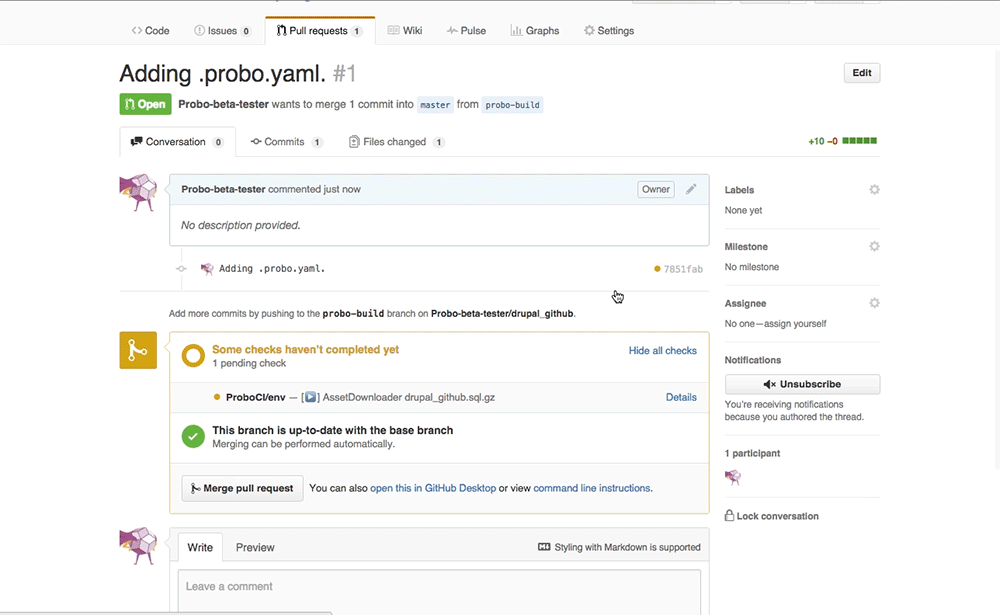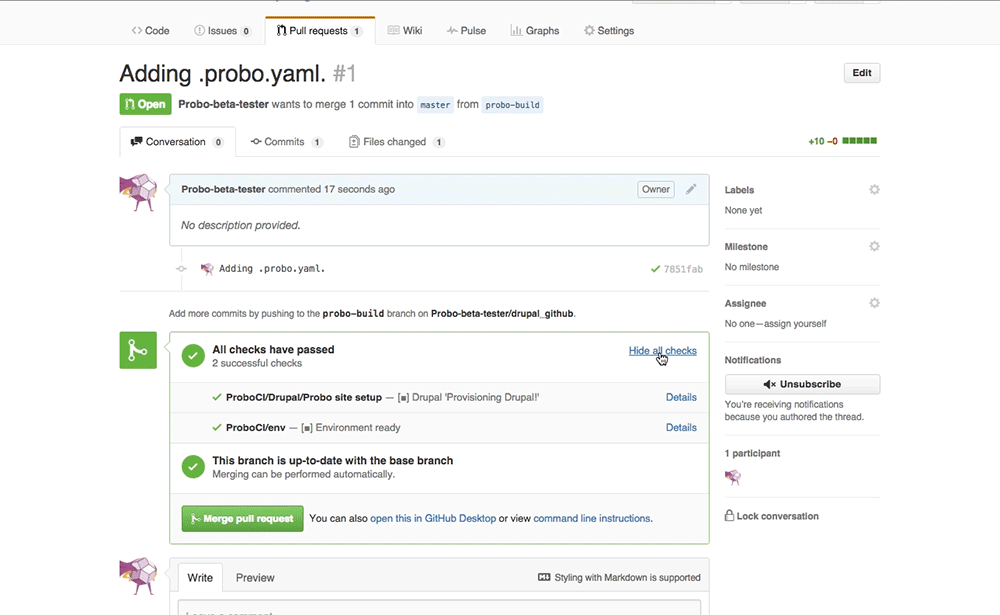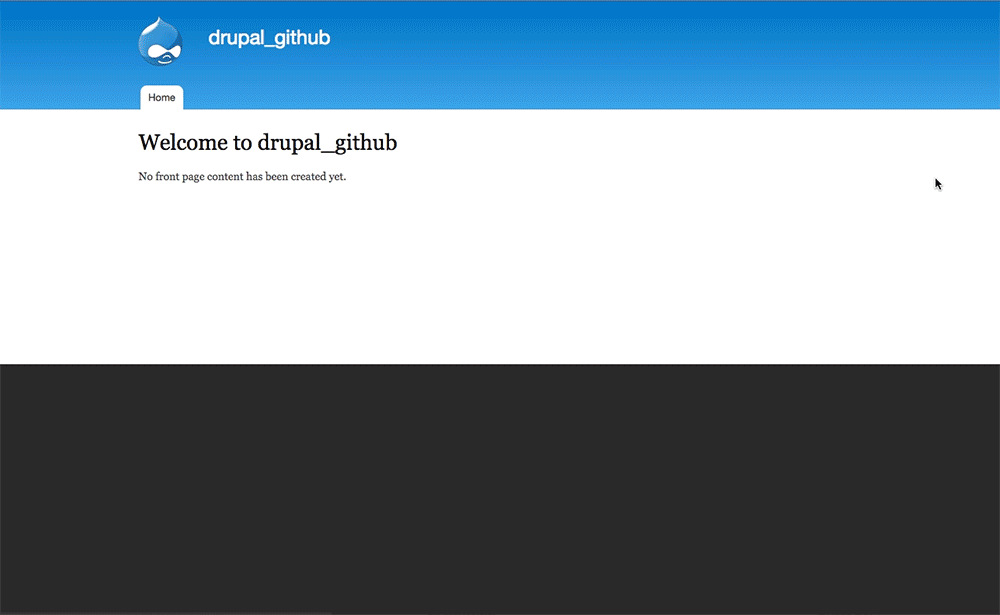
Step 13: Bask in the glory of Probo.CI.
In GitHub you will see the Probo.CI build steps. You can now click on any of the details links and it will direct you back to the Probo.CI dashboard.
Step 14: See your Probo.CI build.
In your Probo.CI dashboard, click on ‘View build’ and your site will open in a new tab. This Probo.build link uses the database defined in your .probo.yaml file and the code from your pull request.
Step 15: Share your Probo.build link with clients, managers, even your parents. Note: It might take a few seconds for your Probo.CI environment to build. Wait until all checks have passed before following your Probo.build link.